Take Profit in Forex

Take profit is a fundamental trading strategy that empowers traders to lock in gains when the price reaches a predetermined level. This automated approach helps manage trades efficiently and provides a structured way to secure profits in an ever-changing market. By removing the emotional aspect of trading, take-profit orders enable traders to adhere to their plans and avoid impulsive decisions. Setting a well-calculated take-profit level is vital for maintaining a balanced risk-reward ratio and fostering long-term success. Understanding how take-profit works, how to set it correctly, and how to calculate the ideal level can enhance a trader’s strategy and discipline, leading to more consistent and profitable outcomes. Whether you're trading stocks, forex, or commodities, mastering take-profit orders can be the key to reducing stress and maintaining focus, allowing you to seize opportunities without the constant pressure of monitoring market fluctuations.
What is the meaning of take-profit?
Take Profit (TP) is one of the fundamental concepts in the world of trading and investing, referring to the practice of setting a specific price level to exit a trade and secure profits. This strategic tool helps traders navigate the unpredictable and often volatile nature of financial markets by ensuring that gains are locked in before potential reversals occur. The essence of Take Profit lies in its ability to remove the emotional element from decision-making. By predefining the point at which a trade will close, traders can maintain discipline, avoid greed, and stick to their overall trading plan. It acts as a safeguard against overextending positions or holding onto trades in the hope of achieving even greater profits, which can sometimes lead to losses if the market moves unfavorably. Incorporating Take Profit into a trading strategy reflects a commitment to structured and calculated decision-making, enabling traders to balance opportunity with risk. It is a tool not just for securing financial gains but also for fostering long-term success in a dynamic and competitive trading environment.
For example, if a trader buys a stock at $50 and sets a Take Profit at $60, the position will close automatically when the price hits $60, securing the $10 profit per share. While this strategy captures profits, it also prevents traders from benefiting further if the market moves beyond the Take Profit level.
How Does the Take-Profit Work?
Take profit orders work automatically when the assets reach the predefined price, which is set by traders. This level represents the price at which the trader wants to secure their profit, ensuring that they capture gains without needing to monitor the market continuously.
Now you can see how it would work:
-
Setting the Take Profit Level:
-
The traders usually set a take-profit price on an opening trade. They would use technical indicators, resistance levels, or desired risk-to-reward ratios that could help them set take profit based on their analysis
-
Order Placement:
-
The take profit order is placed as a conditional order with the broker or trading platform. It is linked to the trade and remains active until the market price reaches the set level or the trader cancels the order.
-
Triggering the Order:
-
When the market reaches the estimated price, the order will be executed automatically.
-
For a buy (Long) position, they have to set the take profit price above the entry price.
-
For a sell (Short) position, the take profit price is set below the entry price.
-
Closure and Profit Secured:
-
When triggered, the trade closes, and the profit is realized in the trader’s account.
What is an Example of a Take Profit?
An example of a take profit can be explained through the following scenario:
Suppose a trader invests in a stock for $50 per share, expecting its value to rise based on market analysis. To secure their profit, the trader sets a take-profit order at $60 per share. This means the trader decides in advance that if the stock price reaches $60, the position will automatically close, capturing a $10 profit per share.
Here’s how it works in practice:
- Entry: The trader buys the stock at $50.
- Setting Take Profit: The trader sets the take-profit level at $60 on their trading platform. This becomes a conditional order tied to their trade.
- Market Movement: Over time, the stock price fluctuates and eventually reaches $60.
- Execution: As soon as the stock price hits $60, the trading platform automatically closes the position. The trader doesn’t need to manually intervene or monitor the market constantly.
- Outcome: The trader secures the $10 per share profit and avoids the risk of the stock price reversing or falling before selling.
This strategy is especially useful in volatile markets, as it ensures the trader captures profits without being overly influenced by emotions or unexpected market movements. However, it also means that if the stock continues to rise beyond $60, the trader won’t benefit from the additional gains, as the position is already closed.
Why Use Take-Profit?
The advantages of using a take-profit order include:
-
Automation:
A take profit order automatically closes your position when the price reaches your target level, so you don’t have to constantly watch the market. -
Emotion Management:
It removes emotional decision-making from the equation, helping traders avoid greed or hesitation that could lead to missed opportunities or losses. -
Discipline and Strategy Alignment:
Take profit orders ensure traders stick to their predefined trading strategy and risk management plan, avoiding impulsive decisions. -
Locks in Gains:
By securing profits at a predetermined price, traders ensure that gains are not lost due to sudden market reversals or increased volatility. -
Efficient Use of Time:
Traders can set take-profit levels and focus on other tasks without needing to constantly monitor price movements. -
Risk-Reward Balance:
When used alongside a stop-loss order, take-profit helps maintain a balanced risk-to-reward ratio, which is critical for long-term trading success. -
Adaptability:
Take profit levels can be adjusted as the trade progresses, allowing traders to respond to new market conditions or updated analyses.
Overall, take profit orders are a valuable tool for traders aiming to manage their trades efficiently, reduce stress, and maintain consistent performance.
How Do You Set Take-Profit?
If I want to show you how MetaTrader 5 (MT5) works with an example, it would be like this:
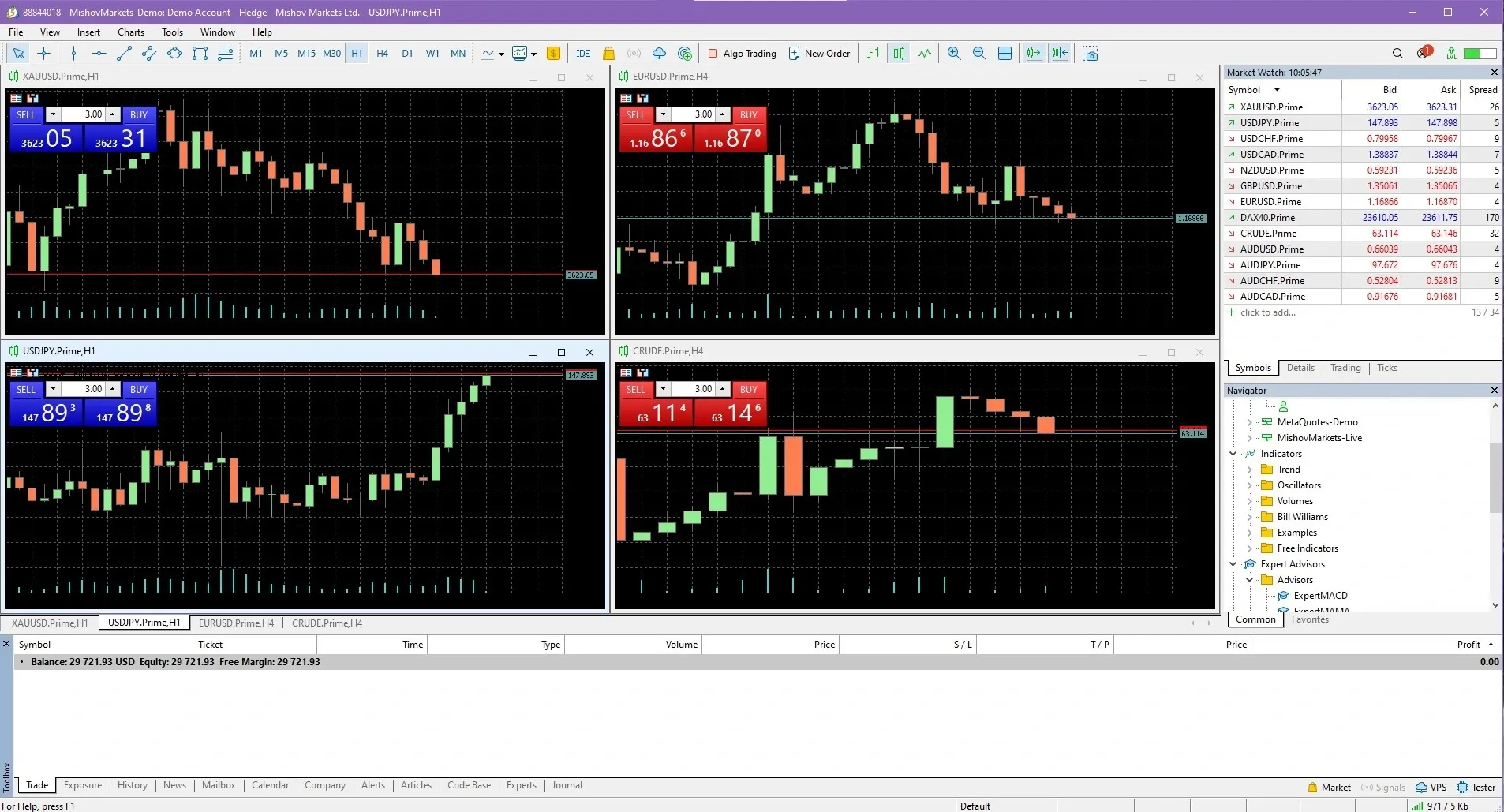
After creating an account with the Mishov Markets broker, you can connect it to MetaTrader 5. Once connected, a screen will open in MT5. Here you can select up to 4 currency pairs of your choice and analyze their chart movements.
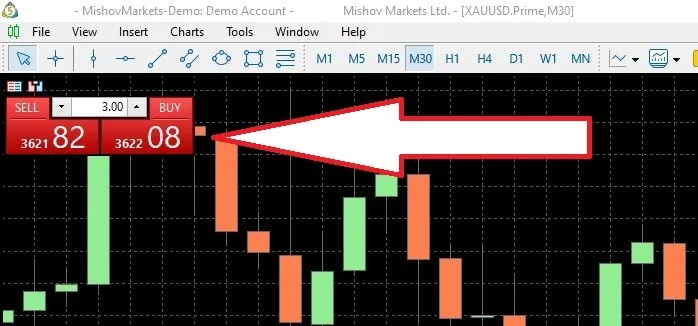
As you can see, in the upper left corner of each chart, you can open a sell or buy position with just one click.
Your position will be marked on the chart with a green line. By clicking on this line and selecting the Modify option, you can set your Take Profit (TP) and Stop Loss (SL) levels.
Alternatively, if you prefer, you can go to the Tools section and select New Order, where you can define your TP/SL levels before entering the trade.
How Do You Calculate the Best Take Profit?
Calculating the best take-profit level involves analyzing factors such as market conditions, the asset’s historical price movements, and your trading strategy. Here’s how to approach it:
1. Set Your Risk-Reward Ratio:
-
Risk-reward ratio is the proportion between the potential risk (loss) and the potential reward (profit) of a trade.
-
A common and effective ratio is 1:2 or higher, meaning for every dollar risked, you aim for two dollars in profit.
-
For example, if your stop-loss level is 50 pips away from your entry, a take-profit level at 100 pips would result in a 1:2 risk-reward ratio.
2. Analyze Support and Resistance Levels:
-
Support levels indicate where the price tends to find buying interest, while resistance levels indicate where selling pressure is usually strong.
-
Setting your take profit near or just before significant resistance levels (for a buy trade) or support levels (for a sell trade) can help you capture profits before the price reverses.
3. Use Technical Indicators:
-
Indicators like Moving Averages, Fibonacci Retracements, and Bollinger Bands can provide insights into potential take-profit levels.
-
For example, a trader might set the take profit at a point where the price historically reverses or where it is likely to meet a moving average.
4. Analyze Volatility:
-
Assess the asset's volatility using tools like the Average True Range (ATR). The ATR helps you understand how much the price typically moves within a given period.
-
For higher-volatility assets, you might want to set a wider take-profit to allow the trade room to move and reach your target.
5. Set a Realistic Profit Target:
-
Base your take-profit level on realistic expectations rather than aiming for an overly ambitious target. If the take profit is set too far, the asset might reverse before reaching your goal.






